This document provides a consolidated summary of the key topics covered in the first week of the AIO 2025 program. The content is organized based on the provided PDF materials, covering essential skills, Python fundamentals, database basics, coding methodologies, and practical exercises.
🎯 1. Skills for AIO 2025
This section outlines the essential skills and tools you’ll need to succeed in your AI research and development journey.
1.1 How to Find and Read Scientific Papers 📖
Effectively finding and understanding research is a cornerstone of AI.
Where to Find Papers:
- Google Scholar: A broad search engine for academic literature
- IEEE Xplore: A digital library focused on technical fields like computer science and electronics
- PubMed: A database for biomedical and life sciences literature
- Preprint Repositories (arXiv, bioRxiv): Access to the latest research before peer review
- Papers With Code: A great resource that links research papers to their corresponding code implementations
- AIO Community: Leverage the collective knowledge of your peers for recommendations and discussions
How to Read Papers (Step-by-Step Roadmap):
📖 Research Paper Reading Roadmap
💡 Reading Strategy: Follow the 7-step sequence for systematic paper comprehension
🎓 Dr Experience - Advanced Reading Method
🎓 Dr's Approach: Strategic 4-stage method for efficient paper analysis
1.2 Making a Research Plan & Documenting Results 📋
- Research Plan: Use AI tools like Gemini to help structure your research. Define your objectives, identify key questions, outline your methodology, and set a timeline
- Documentation: Use Overleaf (LaTeX) for professional-quality scientific documents. LaTeX is the standard for academic papers, giving you precise control over formatting, especially for mathematical equations
1.3 Coding Environment & AI Assistants 💻
Local Environment:
- Jupyter Notebook or Anaconda to set up a powerful local development environment
Cloud Environment:
- Google Colab is an excellent tool that provides free access to GPUs, making it ideal for training machine learning models. You can easily mount your Google Drive to access datasets
AI Coding Assistants:
Leverage tools like Gemini in Colab and ChatGPT to accelerate your workflow. They can help with:
- Generating boilerplate code
- Explaining complex code snippets
- Debugging errors
- Adding comments to your code
- Summarizing articles or concepts
🐍 2. Basic Python
This section covers the foundational elements of the Python programming language, including data types, branching, and a simple rule-based chatbot application.
2.1 Variables and Data Types
In Python, a variable is a container for storing data values. The main data types are:
| Data Type | Description | Example | Memory Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
int | Integer numbers (whole numbers) | 10, -5, 0 | 28 bytes |
float | Floating-point numbers (with decimals) | 3.14, -0.5, 10.0 | 24 bytes |
str | String (sequence of characters) | "Hello", 'Python' | Variable |
bool | Boolean (logical value) | True, False | 28 bytes |
list | An ordered and mutable collection | [1, "apple", 3.14] | Variable |
dict | An unordered collection of key-value pairs | {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 25} | Variable |
📝 Quick Example:
# Variable assignment examplesname = "AIO Student" # strage = 25 # intheight = 1.75 # floatis_student = True # boolskills = ["Python", "SQL"] # listprofile = {"name": name, "age": age} # dict
# Check data typesprint(type(name)) # <class 'str'>print(type(age)) # <class 'int'>2.2 Branching (Conditional Statements) 🌟
Conditional statements allow your program to execute different blocks of code based on whether a condition is True or False.
if: Executes a block of code if its condition is trueelif(else if): Checks another condition if the previous if/elif conditions were falseelse: Executes a block of code if all preceding conditions were false
Syntax:
score = 85
if score >= 90: print("Grade: A")elif score >= 80: print("Grade: B")elif score >= 70: print("Grade: C")else: print("Grade: F")# Output: Grade: B2.3 Functions 🔧
Functions are reusable blocks of code that perform a specific task.
- Built-in Functions: Python provides many useful built-in functions like
print(),type(),int(),len() - User-Defined Functions: You can create your own functions using the
defkeyword
Syntax:
def greet(name): """This function greets the person passed in as a parameter.""" return f"Hello, {name}!"
# Calling the functionmessage = greet("AIO Student")print(message) # Output: Hello, AIO Student!2.4 Application: Rule-Based Chatbot 🤖
A simple chatbot can be created using a series of if-elif-else statements to respond to specific user inputs.
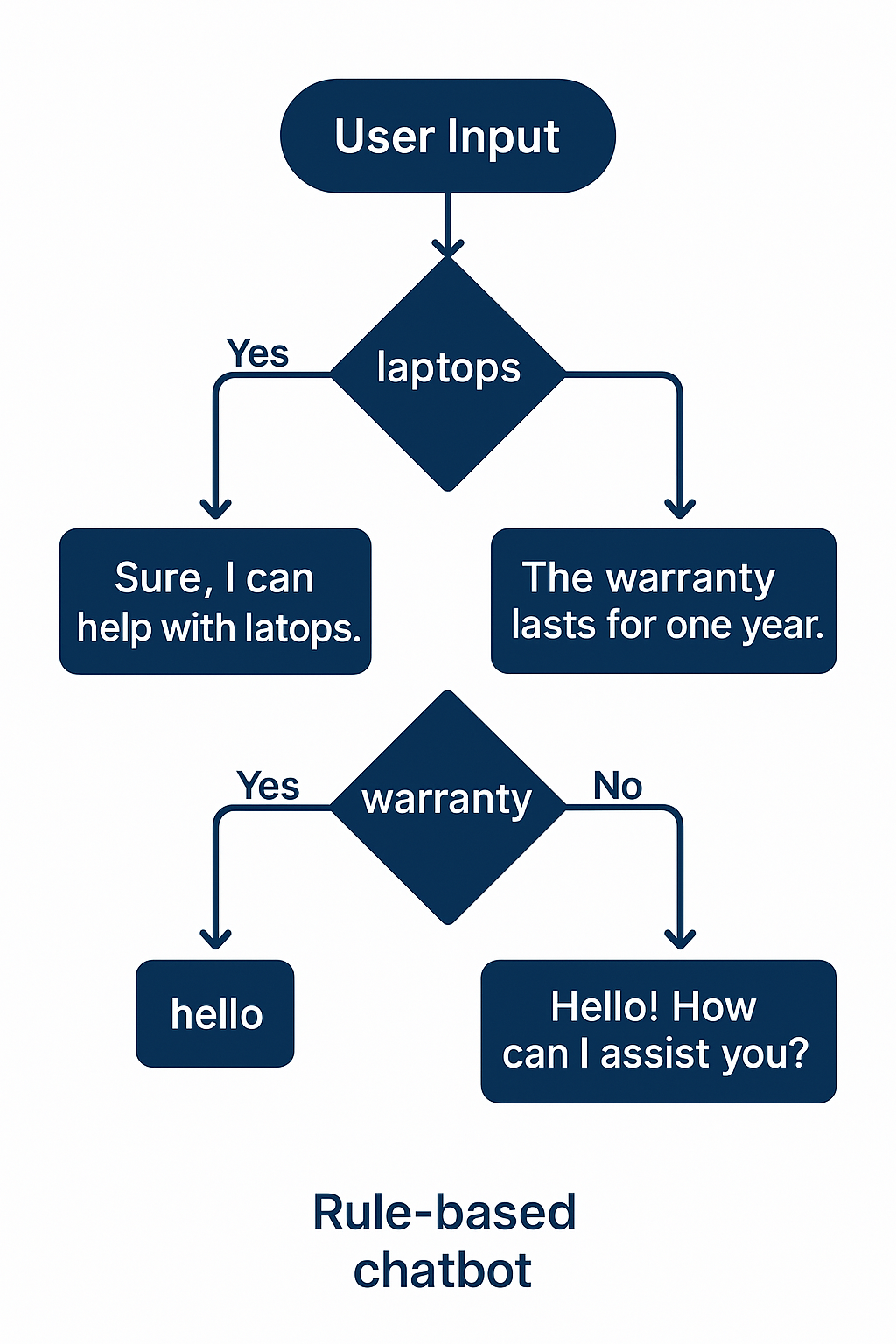
The decision tree approach makes chatbot logic easy to understand and modify. Each condition represents a keyword check, and each leaf node contains the appropriate response. This method works well for simple, rule-based interactions where you can predict common user inputs.
Example Logic:
user_input = "Tell me about laptops"
if "laptops" in user_input: print("We have a wide range of high-performance laptops. What is your budget?")elif "warranty" in user_input: print("Please provide your order number to check the warranty.")elif "hello" in user_input: print("Hello! How can I assist you today?")else: print("I'm sorry, I don't understand. Can you rephrase?")🗃️ 3. Database & SQL (Part 1)
Databases are organized collections of data, and SQL (Structured Query Language) is the standard language used to interact with them.
3.1 What is a Database? 💾
A database is designed for efficient storage, retrieval, and management of data. Instead of storing all information in one massive file (like an Excel sheet), a relational database breaks data into multiple related tables to reduce redundancy and improve integrity.
Key Concepts:
- DBMS (Database Management System): Software that interacts with the user, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL)
- Relational Database: Organizes data into tables with rows and columns. Tables can be linked together using keys
- Primary Key: A unique identifier for each record in a table
- Foreign Key: A key used to link two tables together
📊 E-commerce Database Entity-Relationship Diagram
🔍 Diagram Structure: 4 tables với relationships: CUSTOMERS → ORDERS → ORDER_ITEMS ← PRODUCTS
3.2 Introduction to SQL 📊
SQL is used to perform actions like querying data, inserting new records, updating records, and deleting records.
The SELECT Statement
The SELECT statement is used to query data from a database.
🎯 SQL SELECT Statement Flow
📋 SELECT Columns
- * (All columns)
- Specific columns
- Calculated fields
🗃️ FROM Table
- Single table
- Multiple tables (JOIN)
- Subqueries
🔍 WHERE Conditions
- Filter criteria
- AND/OR logic
- LIKE patterns
📊 ORDER BY
- ASC (ascending)
- DESC (descending)
- Multiple columns
🎯 LIMIT Results
- Top N records
- Pagination
- Performance optimization
💡 Pro Tip: Use LIMIT for large datasets to improve query performance
Select all columns:
SELECT * FROM customers;Select specific columns:
SELECT first_name, last_name, email FROM customers;Using aliases for columns:
SELECT unit_price * 1.1 AS new_price FROM products;Filtering Data with WHERE
The WHERE clause is used to filter records based on a specific condition.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
= | Equal |
!= or <> | Not equal |
> | Greater than |
< | Less than |
>= | Greater than or equal to |
<= | Less than or equal to |
BETWEEN | Between a certain range |
LIKE | Search for a pattern |
IN | To specify multiple possible values |
Combining Conditions: Use AND (both conditions must be true) and OR (at least one condition must be true).
Example:
-- Select customers from Virginia (VA) with more than 1000 pointsSELECT first_name, last_name, pointsFROM customersWHERE state = 'VA' AND points > 1000;Pattern Matching with LIKE
%: Represents zero, one, or multiple characters_: Represents a single character
Example:
-- Select customers whose last name starts with 'B'SELECT * FROM customers WHERE last_name LIKE 'B%';Sorting Results with ORDER BY
The ORDER BY keyword is used to sort the result-set in ascending or descending order.
ASC: Ascending order (default)DESC: Descending order
Example:
-- Select all customers, ordered by points from highest to lowestSELECT * FROM customers ORDER BY points DESC;Limiting Results with LIMIT
The LIMIT clause specifies the maximum number of records to return.
-- Get the top 3 customers with the highest pointsSELECT * FROM customers ORDER BY points DESC LIMIT 3;🔄 4. Loops in Python
Loops are used to execute a block of code repeatedly.
4.1 for Loops 🔁
A for loop is used for iterating over a sequence (like a list, tuple, dictionary, set, or string).
Syntax:
# Iterating over a listfruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]for fruit in fruits: print(fruit)
# Using the range() function# range(5) generates numbers from 0 to 4for i in range(5): print(f"Number: {i}")4.2 while Loops ⏳
A while loop executes a set of statements as long as its condition is true.
Syntax:
count = 0while count < 5: print(f"Count is: {count}") count = count + 1 # Important: update the counter to avoid an infinite loop4.3 Loop Control Statements 🎛️
break: Exits the loop entirely, regardless of the conditioncontinue: Skips the rest of the current iteration and proceeds to the next one
break Example:
# Stop the loop when i is 3for i in range(10): if i == 3: break print(i) # Output: 0, 1, 2continue Example:
# Skip printing the number 3for i in range(5): if i == 3: continue print(i) # Output: 0, 1, 2, 4🏗️ 5. Coding Methodology
Writing high-quality code is crucial for collaboration, maintenance, and scalability. This involves following established conventions and principles.
5.1 Clean Code & PEP-8 ✨
Clean Code:
Code that is easy to read, understand, and maintain by others (and your future self). It should be readable, testable, maintainable, and extensible.
PEP-8:
The official style guide for Python code. Adhering to it ensures consistency and readability. Key rules include:
- Indentation: Use 4 spaces per indentation level
- Line Length: Limit all lines to a maximum of 79 characters
- Whitespace: Use whitespace around operators and after commas, but not directly inside brackets
- Naming Conventions:
snake_case: For functions and variables (e.g.,calculate_total)PascalCase: For classes (e.g.,MyClass)UPPERCASE_SNAKE_CASE: For constants (e.g.,MAX_SIZE)
- Comments & Docstrings: Use comments to explain non-obvious code. Use docstrings to explain what a function, module, or class does
5.2 Pythonic Code 🐍
“Pythonic” means writing code that leverages Python’s unique features to be more readable, concise, and efficient.
List/Dict/Set Comprehensions:
A concise way to create lists, dictionaries, or sets.
# Non-Pythonicsquares = []for i in range(10): squares.append(i*i)
# Pythonicsquares = [i*i for i in range(10)]Context Managers (with statement):
Ensures that resources (like files) are properly managed (e.g., automatically closed), even if errors occur.
# The file is automatically closed after the blockwith open('file.txt', 'r') as f: content = f.read()5.3 General Coding Principles 📏
🏗️ Clean Code Principles
💡 Remember: These principles work together to create maintainable, scalable, and robust code
- DRY (Don’t Repeat Yourself): Avoid duplicating code. Abstract common logic into functions or classes
- KISS (Keep It Simple, Stupid): Prefer simple, straightforward solutions over overly complex ones
- YAGNI (You Aren’t Gonna Need It): Don’t add functionality until it’s actually required. Avoid premature optimization
- SOLID Principles: Design principles for writing maintainable and scalable code
🧪 6. Practical Exercises (Activation Functions & Metrics)
This section summarizes the practical exercises involving the implementation of common functions used in machine learning.
6.1 Exercise 1: Calculate F1-Score 🎯
The F1-Score is a metric used to evaluate a classification model’s accuracy. It is the harmonic mean of Precision and Recall.
-
Precision: Of all the positive predictions, how many were actually correct?
-
Recall: Of all the actual positives, how many did the model correctly identify?
-
F1-Score:
Where:
- TP = True Positives
- FP = False Positives
- FN = False Negatives
6.2 Exercise 2: Calculate Activation Functions ⚡
Activation functions introduce non-linearity into a neural network, allowing it to learn more complex patterns.
Sigmoid:
Maps any value to a range between 0 and 1.
ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit):
Returns 0 for any negative input, and the input value itself for any positive input. It’s computationally efficient and widely used.
ELU (Exponential Linear Unit):
A variant of ReLU that allows negative values, which can sometimes help learning.
Formula: ELU(x) = x if x > 0, else α(e^x - 1) if x ≤ 0
📊 Activation Functions - Simple & Clear
| Function | Formula | When to Use | Why? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sigmoid | 1/(1 + e^(-x)) | Output probabilities | Range: 0-1 |
| ReLU | max(0, x) | Hidden layers | Simple & fast |
| ELU | x if x>0, α(e^x-1) if x≤0 | Deep networks | Smooth curve |
💡 Quick Guide: Start with ReLU → Use Sigmoid for final output → Try ELU for deeper networks
📈 Interactive Activation Functions Visualization
🎯 Activation Functions Interactive Charts
🎮 Interactive: Hover over lines to see exact values • Professional mathematical visualization with D3.js
6.3 Exercise 3: Calculate Loss Functions 📉
Loss functions measure how well a model’s prediction matches the actual target value. The goal of training is to minimize this loss.
MAE (Mean Absolute Error):
The average of the absolute differences between predictions and actual values.
MSE (Mean Squared Error):
The average of the squared differences. It penalizes larger errors more heavily than MAE.
6.4 Exercise 4: Estimate Trigonometric Functions 📐
Trigonometric functions like sin(x) and cos(x) can be approximated using their Taylor series expansions. This is a great exercise in using loops and factorials.
Sine Approximation:
Cosine Approximation:
This requires implementing a factorial function and then summing the terms of the series in a loop.
📊 Interactive Taylor Series Visualization
📐 Taylor Series Approximation Progress
● Term 1: sin(x) ≈ x
Basic linear approximation
● Term 2: + x³/3!
Cubic correction term
● Term 3: + x⁵/5!
Fifth order term
● Term 4: + x⁷/7!
Seventh order term
● Term 5+: Higher Orders
x⁹/9! + x¹¹/11! + ...
🔍 Key Insight: Each additional term dramatically improves accuracy, especially for values further from x=0
📊 Taylor Series Accuracy Comparison for sin(π/4) ≈ 0.7071:
| Terms | Formula | Approximation | Error | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | x | 0.7854 | 0.0783 | ❌ Poor |
| 2 | x - x³/6 | 0.6846 | 0.0225 | ⚠️ Fair |
| 3 | x - x³/6 + x⁵/120 | 0.7071 | 0.0000 | ✅ Good |
| 4 | + x⁷/5040 | 0.7071 | 0.0000 | ✅ Excellent |
🎯 Key Insights:
- More terms = Higher accuracy especially away from x=0
- Convergence radius determines where series works well
- Computational trade-off between accuracy and speed
The Taylor series expansion is a powerful mathematical tool that allows us to approximate complex functions using polynomial terms. As shown in the progression above, adding more terms progressively improves the accuracy of the approximation. This concept is fundamental in numerical computing and machine learning algorithms where exact calculations may be computationally expensive.
🛠️ 7. Development Environment Setup
7.1 Python Environment Management
🛠️ Python Development Environment Ecosystem
🐍 Python Development
Foundation for AI/ML Development
💻 Local Environment
📦 Anaconda Distribution
→ Package Management
🏗️ Virtual Environments
→ Isolated Dependencies
📔 Jupyter Notebook
→ Interactive Development
☁️ Cloud Environment
🔬 Google Colab
Free GPU/TPU access
🚀 Replit
Collaborative coding
📊 Codespaces
GitHub integration
🎯 Recommendation: Start with Google Colab for learning, then transition to local Anaconda setup for serious projects
Recommended Setup:
# Install Anaconda (includes Python + popular packages)# Download from: https://www.anaconda.com/download
# Create virtual environmentconda create -n aio2025 python=3.11conda activate aio2025
# Install essential packages for AIpip install numpy pandas matplotlib scikit-learn jupyter7.2 Essential AI Libraries
| Library | Purpose | Installation |
|---|---|---|
| NumPy | Numerical computing | pip install numpy |
| Pandas | Data manipulation | pip install pandas |
| Matplotlib | Data visualization | pip install matplotlib |
| Scikit-learn | Machine learning | pip install scikit-learn |
| TensorFlow | Deep learning | pip install tensorflow |
| PyTorch | Deep learning | pip install torch |
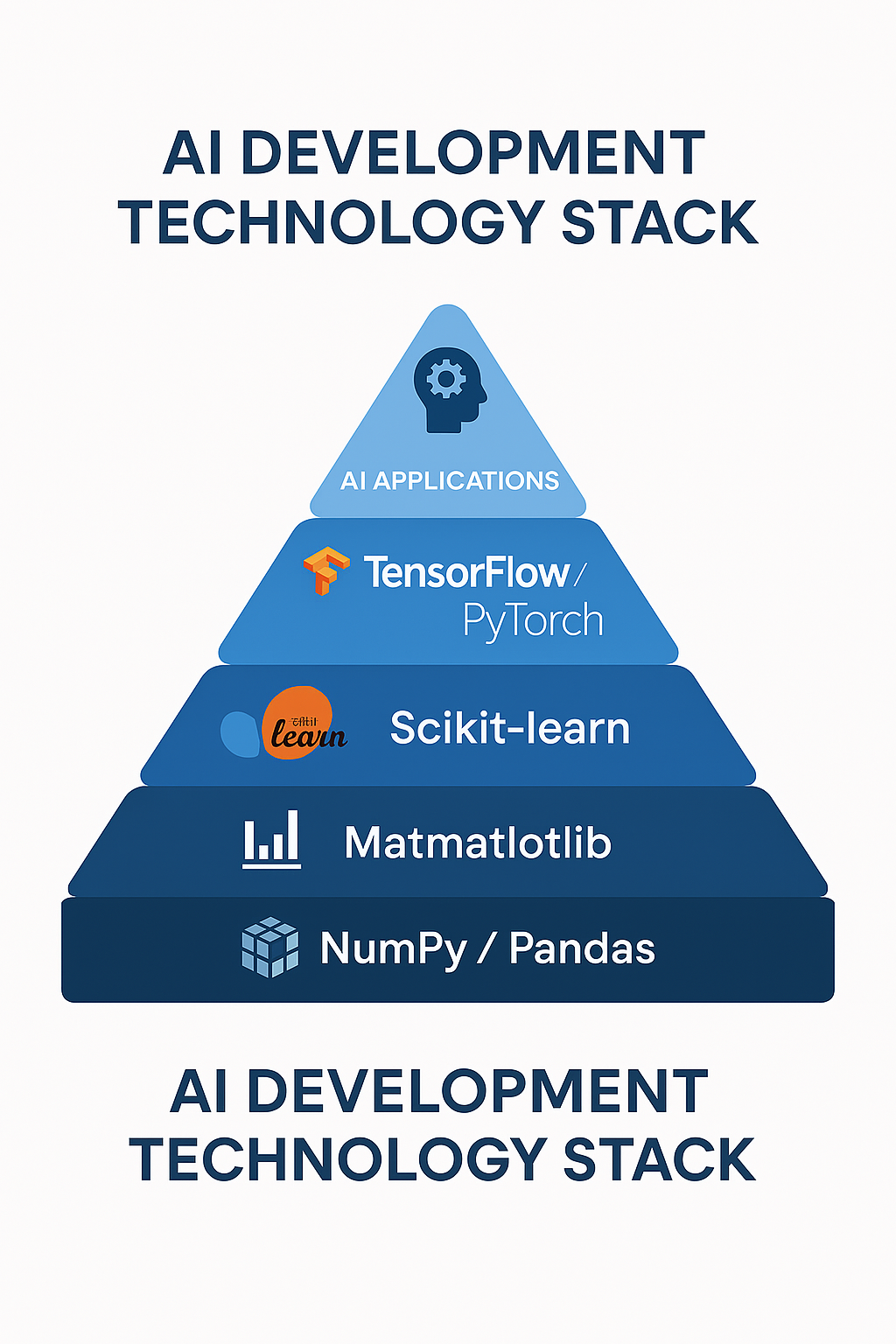
The AI development stack follows a hierarchical structure where each layer builds upon the previous one. Python serves as the foundation language, providing the syntax and basic functionality. NumPy and Pandas handle numerical computing and data manipulation respectively. Matplotlib enables data visualization, while Scikit-learn provides traditional machine learning algorithms. At the top, TensorFlow and PyTorch offer deep learning capabilities for building neural networks and advanced AI applications.
Understanding this stack progression helps you learn systematically - master the fundamentals before moving to more complex libraries. Each tool has its specialized purpose in the AI development workflow.
📊 8. Learning Progress Tracker
8.1 Week 1 Skills Checklist
📅 Week 1 Learning Timeline & Progress
🔍 Research Skills
🐍 Python Basics
🗃️ Database & SQL
🏗️ Coding Standards
🧮 AI Mathematics
🎉 Week 1 Complete! All learning objectives achieved on schedule
8.2 Self-Assessment Matrix
| Skill Area | Beginner (1-2) | Intermediate (3-4) | Advanced (5) | My Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper Reading | Can skim abstracts | Uses 3-pass method | Critical analysis | ⭐⭐⭐___ |
| Python Basics | Basic syntax | Control flow + functions | OOP + advanced | ⭐⭐⭐⭐_ |
| SQL Queries | SELECT statements | JOINs + filtering | Complex queries | ⭐⭐⭐___ |
| Clean Code | Basic formatting | PEP-8 compliance | Design patterns | ⭐⭐⭐___ |
| AI Math | Basic formulas | Implementation | Optimization | ⭐⭐_____ |
🎯 Week 1 Summary
Week 1 of AIO 2025 has provided a solid foundation in:
✅ Research Skills: Paper reading and documentation strategies
✅ Python Fundamentals: Variables, functions, control flow
✅ Database Basics: SQL queries and data management
✅ Code Quality: Clean coding practices and methodologies
✅ AI Mathematics: Activation functions, metrics, and approximations
📚 Next Steps & Action Plan:
🎯 Next Steps & Action Plan
🎉 Week 1 Complete
Foundations established, ready for next phase
💻 Practice Coding
⚙️ Setup Environment
📚 Read AI Papers
🚀 Week 2 Ready
Advanced Python, ML fundamentals, first AI model
⏰ Timeline: Complete all branches within 24-48 hours for optimal momentum into Week 2
🎯 Immediate Actions (Next 24 hours):
-
Setup Development Environment
- Install Anaconda/Python 3.11
- Create
aio2025virtual environment - Install essential libraries
-
Practice Coding
- Implement F1-Score calculator
- Code activation functions (Sigmoid, ReLU, ELU)
- Create Taylor series approximations
-
Start Paper Reading
- Find 1 AI paper related to your interests
- Apply the 3-pass reading method
- Document key insights
📈 Week 2 Preparation:
- Review and strengthen any weak areas identified in self-assessment
- Prepare questions for upcoming lectures
- Set up a learning journal to track daily progress
🏆 Key Achievements Unlocked:
✅ Research Foundation: Master the art of finding and reading scientific papers
✅ Python Proficiency: Understand core programming concepts and syntax
✅ Database Basics: Query data effectively with SQL
✅ Code Quality: Write clean, maintainable Python code following PEP-8
✅ AI Mathematics: Implement activation functions, loss functions, and metrics
✅ Environment Setup: Ready to develop AI applications
💡 Weekly Reflection Questions:
- What was the most challenging concept this week?
- Which skill do you want to improve most?
- How will you apply these fundamentals in future projects?
- What questions do you have for Week 2?
🔗 Additional Resources:
- Python Practice: LeetCode, HackerRank
- SQL Practice: SQLBolt, W3Schools SQL
- AI Papers: ArXiv, Papers With Code
- Documentation: Python Docs, NumPy Docs
Week 1 knowledge synthesis completed. Foundation built. Ready to advance to Week 2 topics! 🚀
Next Post Preview: Week 2 will cover advanced Python concepts, machine learning fundamentals, and your first AI model implementation!